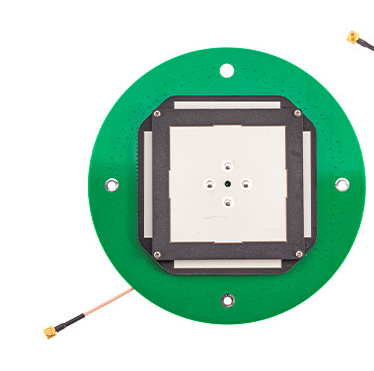
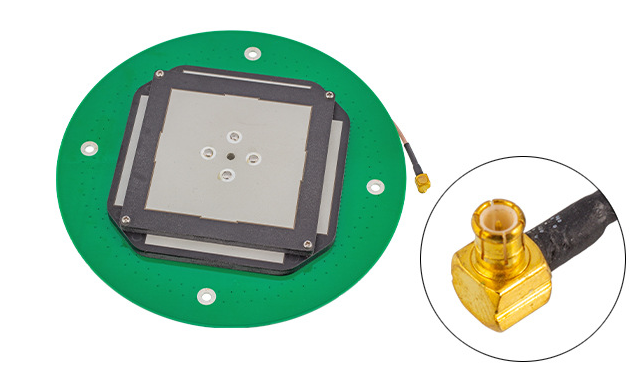
Gps antenna index
With the wide application of Global Positioning system (GPS) technology, as the key equipment to receive GPS signals, the performance of GPS antenna directly affects the positioning accuracy and reliability. This paper will introduce the key indicators of GPS antenna in detail to help readers better understand and select GPS antennas that meet their own needs.
Overview of GPS Antenna

GPS antenna is a device that receives GPS satellite signals. Its main function is to convert weak GPS signals into processable electrical signals. The performance of GPS antenna directly affects the positioning accuracy and stability of GPS receiver.
Key indicators of GPS antenna
1. Gain (Gain)
The gain refers to the ability of the antenna to receive the signal. The higher the gain of the GPS antenna, the greater the signal strength received and the higher the positioning accuracy. When selecting the GPS antenna, the appropriate gain should be selected according to the use environment and requirements.
2. Axis ratio (Axial Ratio)
The axis ratio refers to the ratio of the main polarization to the cross polarization of the antenna in the maximum radiation direction. excellent axis ratio performance can improve the circular polarization performance of the antenna and help to maintain a stable signal reception in a complex environment.
3. Polarization mode (Polarization)
The polarization of GPS signals is usually circularly polarized, so the polarization of GPS antennas should also be circularly polarized. Circularly polarized antennas can receive signals of horizontal or vertical polarization, which is suitable for a variety of environments.
4. Frequency range (Frequency Range)
The frequency range of GPS signal is L1 (1575.42MHz), L2 (1227.6MHz), etc. When selecting GPS antenna, you should ensure that the frequency range of the selected antenna covers the desired GPS signal frequency.
5. Impedance matching (Impedance Matching)
Impedance matching refers to the matching degree between antenna and transmission line. Good impedance matching can reduce signal reflection and improve signal transmission efficiency. When selecting GPS antenna, we should ensure that the impedance of the antenna matches the transmission line.
6. Receiving Angle (Receiving Angle)
The receiving angle refers to the azimuth range of the signal received by the GPS antenna, and the larger receiving angle helps to improve the signal receiving ability of the antenna in the complex environment.
7. Noise performance (Noise Performance)
Noise performance refers to the ability of the antenna to resist external noise when receiving signals. Excellent noise performance can improve the positioning accuracy and stability of the antenna.
8. Stability (Stability)
Stability refers to the ability of GPS antenna to maintain stable performance in the environment of temperature change and vibration. Stable GPS antenna helps to improve positioning accuracy and reliability.
9. Volume and weight (Size and Weight)
According to the application scenarios and requirements, the appropriate volume and weight of the GPS antenna are selected. The vehicle-mounted GPS antenna usually needs smaller size and lighter weight for installation and use.
Selecting a suitable GPS antenna needs to consider many indexes, including gain, axis ratio, polarization mode, frequency range, impedance matching, receiving angle, noise performance and stability, etc. In practical application, we should comprehensively consider according to the use environment and requirements, select the GPS antenna with excellent performance, stability and reliability, and pay attention to the volume and weight of the GPS antenna in order to install and use reasonably in the practical application.
Application example
1. Vehicle navigation: the vehicle GPS antenna needs to have high gain and receiving angle in order to maintain stable signal reception during driving, and the volume and weight of the antenna also need to be suitable for the vehicle environment.
2. Aerospace: the aerospace field requires extremely high performance of GPS antennas, so it is necessary to select GPS antennas with high gain, excellent axis ratio and stable performance to ensure high-precision positioning in complex environments.
3. Outdoor exploration: when exploring outdoors, you can choose portable GPS antenna to pay attention to its portable, anti-falling and noise performance, in order to achieve accurate positioning in the outdoor environment.
Purchase suggestion
1. Understand the scenarios and requirements of the application, and determine the appropriate type of GPS antenna.
2. Compare different brands and models of GPS antennas, and pay attention to their performance index and practical application evaluation.
3. Choose brands and suppliers with stable supply capacity and good after-sales service.
4. Conduct actual testing or experience before purchase to ensure that the selected GPS antenna meets the actual requirements.
Concluding remarks
In this paper, the key indexes of GPS antenna are introduced in detail, including gain, axis ratio, polarization mode, frequency range, impedance matching, receiving angle, noise performance and stability. It is hoped that readers can better understand and select the GPS antenna suitable for their own needs and provide stable and reliable positioning services for practical applications.