The basic principle and design of circular PCB antenna
Circular PCB Antenna – A Deep Dive into Knowledge
With the exponential growth of wireless communication systems, the design and development of compact and efficient antennas have become a critical research area for communication engineers. Among various types of antennas, the circular PCB antenna has gained considerable attention due to its compactness, low fabrication cost, and omnidirectional radiation pattern. In this paper, we will explore the fundamental principles, design considerations, and performance characteristics of a circular PCB antenna.
Fundamental Principles of Circular PCB Antenna:
A circular PCB antenna is a type of microstrip antenna that operates on the microstrip line's principle. The microstrip line consists of a metallic strip of width (w) and thickness (t) printed on a dielectric substrate with a thickness (h). The substrate material's dielectric constant (εr) affects the wave propagation velocity and, therefore, the antenna's resonant frequency. The PCB antenna's radiating patch is usually circular in shape and connected to feed lines that provide the necessary excitation for radiation. The circular patch's diameter (D) determines the radiation properties, and the distance between the patch and the ground plane (h) alters the radiation pattern shape.
Design Considerations:
The design considerations for circular PCB antenna include selecting the substrate material, determining the antenna's size and shape, and optimizing the antenna's impedance matching with the feeding line. The substrate material's dielectric constant (εr) and thickness (h) determine the antenna's resonant frequency, bandwidth, and radiation efficiency. Higher dielectric substrates result in higher resonant frequencies, while thinner substrates offer broader bandwidth. The patch's size and shape determine the radiation pattern and impedance matching. For omnidirectional radiation, a circular patch is preferred, and for directional radiation, an elliptical or rectangular patch is suitable. The feeding line's impedance and length affect the impedance matching and operating frequency. THere are different feeding mechanisms used for circular PCB antennas, such as microstrip line, coaxial probe, and aperture coupling.
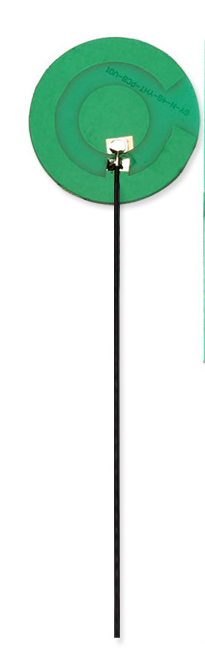
Performance Characteristics:
The performance of a circular PCB antenna is evaluated based on various parameters, such as radiation efficiency, bandwidth, gain, and radiation pattern. The antenna's radiation efficiency is determined by the substrate's dielectric constant and losses in the feeding mechanism. The bandwidth of a circular PCB antenna is generally narrow, typically less than 10% of the resonant frequency, but it can be enhanced by optimizing the feeding mechanism and ground plane design. The gain of a circular PCB antenna is relatively low compared to other types of antennas due to its compact size. Still, it can be improved by using higher dielectric substrates, optimizing the patch size and shape, and using more efficient feeding and ground plane designs. The radiation pattern of a circular PCB antenna is usually omnidirectional, but it can be altered by changing the patch and ground plane's geometry.
Conclusion:
the circular PCB antenna is a compact and efficient antenna suitable for wireless communication systems. The fundamental principles, design considerations, and performance characteristics of this type of antenna have been discussed in this paper. The antenna's design and optimization require careful consideration of substrate material, patch size and shape, feeding mechanism, and ground plane design to achieve a desired resonant frequency, bandwidth, gain, and radiation pattern. The circular PCB antenna's extensive use in various wireless communication systems demonstrates its potential to provide reliable and cost-effective connectivity solutions.





